Highlights: The controversy on the timeline of totally autonomous automobiles touring on US highways rages on, with the optimists within the business predicting preliminary functions to start as early as 2019 and the skeptics questioning whether or not 2035 is a practical launch date.
Specialists agree that self-driving automobiles current the auto insurance coverage business with main challenges, but additionally with important near-term alternatives.
The best potential of automated automobiles within the brief time period will derive from the huge quantities of information they create. Autonomous-vehicle producers, software program corporations and insurers will all be taken with analyzing this information not solely to enhance current merchandise, but additionally to develop new value-added providers. As well as, billions of {dollars} in premium income might be out there to these carriers which are first to launch insurance coverage providers for this new danger class.
Introduction:
On this information, we’ll cowl:
What will we imply by ‘autonomous’
Who’s making self-driving automobiles and autonomous-driving expertise?
Regulation of self-driving automobiles
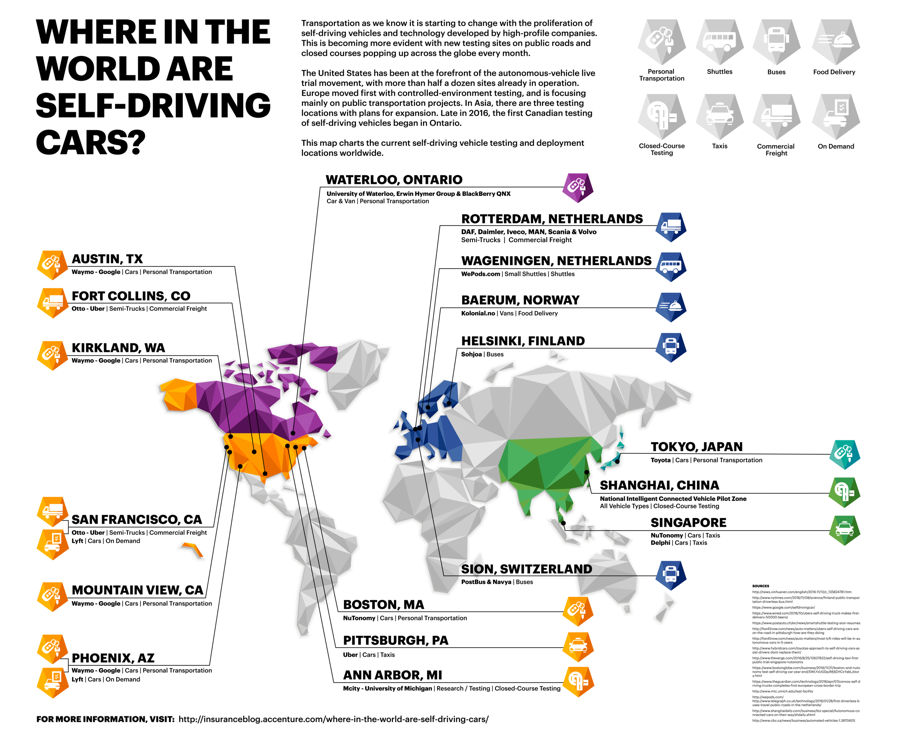
The place are the testing areas for self-driving automobiles?
What do self-driving automobiles imply for the auto insurance coverage business?
Self-driving automobiles and large information
The human ingredient and client attitudes towards driverless automobiles
The takeaway for insurers
The race for self-driving automobiles has been accelerating considerably within the final two years with extra pilot packages popping up throughout the globe and extra auto producers and expertise corporations moving into the sector.
Whereas most consultants agree vast client adoption continues to be years away, from a expertise perspective the launch date for totally automated self-driving automobiles might be as early as 2019 in preliminary functions comparable to public transit or ride-hailing providers.
How briskly these autonomous automobiles will get to the purpose of widespread adoption might be impacted by quite a few elements along with expertise. These embrace regulation and laws, the safety of the information these automobiles must function, the ecosystem of supporting industries, together with insurance coverage, and naturally client attitudes and ethics.
What will we imply by ‘autonomous’?
In keeping with the Society of Automotive Engineers, there are 5 ranges of automated automobiles:
Degree 1: Driver Help. The motive force controls the car, however good options allow the automobile to alert the driving force to circumstances, the atmosphere and obstructions.
Degree 2: Partial Automation. The car has mixed automated capabilities, i.e. acceleration and steering, however the driver stays engaged.
Degree 3: Conditional Automation. The car manages most safety-critical driving capabilities, however the driver have to be able to take management of the car always.
Degree 4: Excessive Automation. The car is able to performing all safety-critical driving capabilities, however the driver has the choice to regulate the car.
Degree 5: Totally Autonomous. The car is totally driverless and won’t characteristic driving gear.
Degree 4 is the “totally automated self-driving automobiles” to which consultants refer at the moment.
Who’s making self-driving automobiles and autonomous-driving expertise?
The clear chief within the business is Google’s Waymo, which has carried out 5 million highway miles of testing in 25 cities and plenty of extra in laptop simulation. Its principal fleet is comprised of Chrysler Pacificas, though key companions embrace Fiat, Jaguar and Honda ‒ and Lyft.
Among the many auto producers are well-known gamers comparable to Audi, Chrysler, Daimler, Ford, GM, Hyundai, Toyota, Volkswagen and Volvo, however there are additionally loads of newcomers comparable to Faraday Function, Native Motors, Lucid, and NextEV.
Altimeter Group, in its report titled “The Race to 2021: The State of Autonomous Automobiles and a “Who’s Who” of Business Drivers,” gave detailed profiles of all auto producers concerned in autonomous-vehicle expertise and growth. It additionally featured some 50 {hardware} and software program corporations actively creating varied parts for autonomous automobiles. Tech giants Microsoft, Apple, Google and China’s Baidu have been main the self-driving applied sciences, however there are numerous startups comparable to Comma.ai, Drive.ai and Oryx Imaginative and prescient getting concerned.
Regulation of self-driving automobiles
In 2017, the U.S. Division of Transportation (DOT) issued a set of voluntary pointers, known as “A Imaginative and prescient for Security 2.0,” offering suggestions and options for business’s consideration and dialogue. They’re designed to unify the event of automation options, together with full autonomy and superior driver help techniques (ADAS), and to assist unify business, native, state and federal authorities efforts to that finish. The steering additionally streamlines the self-assessment course of for corporations and organizations. “This Steering is fully voluntary, with no compliance requirement or enforcement mechanism. The only goal of this Steering is to help the business because it develops greatest practices within the design, growth, testing, and deployment of automated car applied sciences,” the company famous.
Earlier in 2016, the DOT had launched 15 benchmarks automakers would wish to satisfy earlier than autonomous automobiles hit the highway. It additionally asserted the rights of every US state to control insurance coverage. The coverage report, “Federal Automated Automobiles Coverage: Accelerating the Subsequent Revolution in Roadway Security,” addressed the roles of the federal and state governments in regulating the rising self-driving car expertise and issued this assertion about legal responsibility: “States are answerable for figuring out legal responsibility guidelines for extremely automated automobiles (HAVs). States ought to think about learn how to allocate legal responsibility amongst HAV homeowners, operators, passengers, producers, and others when a crash happens. For instance, if an HAV is decided to be at fault ina crash then who needs to be held liable? For insurance coverage, states want to find out who (proprietor, operator, passenger, producer, and so forth.) should carry motorized vehicle insurance coverage. Willpower of who or what’s the “driver” of an HAV in a given circumstance doesn’t essentially decide legal responsibility for crashes involving that HAV. For instance, states might decide that in some circumstances legal responsibility for a crash involving a human driver of an HAV needs to be assigned to the producer of the HAV.”
This led to the introduction of a flurry of payments (greater than 50 payments in 20 states) in 2017 offering some extent of regulation of self-driving automobiles. Twenty-two states and Washington, D.C., have both handed laws or adopted laws by a governor’s govt order.
In the summertime of 2017, the primary main U.S. invoice on self-driving automobiles, the ‘‘SELF DRIVE Act,” obtained approval from the Power and Commerce Committee within the Home of Representatives. The bipartisan invoice “would enable automobile producers to place as much as 25,000 autonomous automobiles on the roads within the first yr of deployment. Over three years, that quantity would enhance to a 100,000 annual cap. These automobiles wouldn’t be required to satisfy current automobile security requirements.”
A U.S. Senate panel handed one other invoice, the “AV START Act,” two months later, barring states from imposing regulatory roadblocks and clearing the trail for using autonomous automobiles. The Commerce, Science and Transportation Committee unanimously permitted the measure, which might enable automakers to win exemptions for self-driving automobiles from security guidelines that require automobiles to have human controls. States may set guidelines on registration, licensing, legal responsibility, insurance coverage and security inspections, however not efficiency requirements.
Throughout the globe, U.Okay., Germany, South Korea and Singapore have enacted laws permitting autonomous automobiles to be examined on public roads, with China shut behind. “These nations are outpacing the U.S., the place the absence of nationwide laws to make clear a checkerboard of state guidelines hampers the deployment of driverless automobiles,” in response to Bloomberg. In Europe, the U.Okay. is main in shaping a conducive atmosphere for testing, with 4 cities permitting public trials. France and Israel enable checks on their public roads on a case-by-case foundation.
The place are the testing areas for self-driving automobiles?
California tops the listing of driverless-car testing areas in North America, making it the biggest open check floor on this planet. The state adopted laws for testing on public roads in September 2014, and an modification in February allowed testers to check out the automobiles with no security driver on board. Texas and Arizona have been shut behind due their temperate climes, however after the deadly crash in Tempe earlier this yr, Uber suspended all driverless-car testing in Arizona.
Earlier this yr, Michigan turned dwelling to the world’s first freeway testing facility for driverless automobiles. The American Middle for Mobility (ACM) is a non-profit consortium backed by Michigan’s Division of Transportation, the College of Michigan, different state-sanctioned teams, in addition to main companies. The brand new freeway division is part of the 500-acre headquarters and testing grounds of the middle, and features a 2.5-mile loop, with on- and off-ramps, a 230-yard curved tunnel, buyer storage and operations middle. The out of doors facility will even allow automakers to check automobiles in winter driving circumstances.
DOT has a pilot program at 10 areas throughout the U.S., from Iowa Metropolis to central Florida, to check autonomous automobiles in partnership with universities, cities and state departments of transportation.
Whereas North America nonetheless spearheads the motion, there are many testing areas in Europe and Asia. European self-driving car checks have a tendency to focus on public transportation in locations comparable to Finland, Switzerland and the Netherlands. In Asia, Shanghai boasts a closed course, whereas Singapore is dwelling to self-driving taxi service pilot route.
South Korea permits testing on 200 miles of public roads and is supporting building of a check circuit south of Seoul, set to open this yr, Bloomberg reported. Hyundai, Samsung Group, Volkswagen Group and Seoul Nationwide College and others are testing greater than 40 driverless automobiles on public roads.
What do self-driving automobiles imply for the auto-insurance business?
Whether or not self-driving automobiles current a risk or a chance to auto insurers has been the subject of many debates and analysis papers within the final couple of years.
“Autonomous expertise will in the end change the complete automotive business and its supporting ecosystems and provide chains, possession, financing and insurance coverage,” wrote Brian Solis within the Altimeter report. “With the autonomous business racing from zero to warp velocity, each side of the driving world is about for innovation and transformation.”
Warren Buffett informed CNBC that when autonomous automobiles change into commonplace insurance coverage prices would plummet. Nonetheless, he famous that disrupting a complete business would take time.
“If I needed to take the over and underneath [bet] 10 years any longer whether or not 10 % of the automobiles on the highway can be self-driving, I’d take the underneath, however I may very simply be fallacious,” he stated. “It’s one thing that billions and billions and billions are spent on, and brains are being concerned in it, so it may simply come ahead of I feel. And it will likely be destructive for auto insurers.”
A report by Morgan Stanley predicted that disruptors may seize 20 % of the auto insurance coverage market. The evaluation, based mostly on a client survey carried out in collaboration with Boston Consulting Group, discovered that greater than 26 % of the respondents stated they might buy auto insurance coverage from Apple, Google, and even AT&T and Verizon.
“Widespread adoption of autonomous automobiles will fully rework the motor insurance coverage sector in the long run as legal responsibility shifts in direction of producers and the normal danger pool shrinks,” London-based Fitch Scores famous in its driverless-car research.

Our Insuring Autonomous Automobiles report, based mostly on analysis from Stevens Institute of Expertise, concurs: “As many as 23 million totally autonomous automobiles might be touring US highways by 2035. [This] presents the car insurance coverage business with main challenges, but additionally with a major near-term alternative.”
Leveraging this chance would require a significant cultural shift in insurance coverage organizations, our report contends. It additionally highlights the areas with essentially the most favorable potentialities: 1) cybersecurity, 2) product legal responsibility insurance coverage for {hardware} and software program, and three) insuring towards infrastructure issues. Insurers taking motion now will, our report finds, have an necessary first-mover benefit, not solely over different insurers, but additionally towards new disruptors.
Munich Re is one such large participant that determined to make an early transfer and partnered with a self-driving taxi service in California. The startup Voyage has been working trials in Villages Golf and Nation Membership, a retirement group in San Jose. “The settlement to supply self-driving automobile rides within the retirement group nearly fell aside when negotiations hit an deadlock over insurance coverage,” in response to an article in The New York Occasions. “California requires autonomous automobiles to have $5 million of protection, however the Villages insisted on 50 % extra protection as a result of it’s a non-public group with extra legal responsibility danger.” Munich Re stepped as much as the plate, with one request from Voyage: to offer all sensor information, so the insurer may higher perceive the potential dangers.
Expertise Imaginative and prescient for Insurance coverage 2018, our international survey of enterprise and IT executives, offers a have a look at how insurers view autonomous automobiles at the moment and the potential round them.
Self-driving automobiles and large information
Self-driving automobiles generate quite a lot of information and want quite a lot of information with which to function.
Brink journal put it boldly: “Addressing issues relating to information is vital to the way forward for autonomous automobiles. In actual fact, the method to information use and information governance points for autonomous automobiles might help inform different expertise innovators as they, too, look to generate, accumulate, retailer, analyze, and monetize huge quantities of information.”
Autonomous car producers, the software program corporations that create the machine studying techniques, and insurers will all be taken with analyzing this information to not solely enhance current merchandise, but additionally to develop new value-added providers. Brink estimates the potential worth of information generated by autonomous automobiles to achieve $1.5 trillion by 2030, including: “Large information and autonomous automobiles make an ideal match. Throughout operation, autonomous automobiles will generate information that automakers or suppliers might use to enhance security, cut back the period of time spent driving, and decrease the price of working a car. On the identical time, information might be used for analysis and growth or to optimize and customise advertising based mostly on a holistic customer-value administration method.”
Final yr, Toyota introduced its partnership with The Massachusetts Institute of Expertise Media Lab and a wide range of startups to look into how blockchain expertise could also be utilized to driverless automobiles. Toyota’s companions embrace BigChainDB based mostly in Germany; Commuterz in Israel; Oaken Improvements of Dallas and Toronto; and Los Angeles-based Gem. Different automobile and expertise corporations need to crowd-sourced maps for extra correct navigation instruments for self-driving automobiles. BMW, Intel, Mobileye and Right here have partnered in a venture that may harness every day digital camera photos from hundreds of thousands of automobiles and develop a map that may be up to date every day.
The human ingredient and client attitudes towards driverless automobiles
Whereas the keenness of auto producers and tech corporations is amping up, client confidence in self-driving automobiles appeared to lag behind at first. Drivers cited security issues and affordability as the primary causes for his or her hesitance.
Then the tide began to show. A Cornell College analysis research discovered that the common driver can be keen to pay practically $5,000 extra for a completely automated car.
One other survey by American Worldwide Group (AIG) discovered that People are just about evenly divided about driverless automobiles: Forty-one % of survey respondents stated they’re uncomfortable with the concept of sharing the highway with driverless automobiles, whereas 42 % have been typically OK with it.
A big majority (75 %) of respondents anxious that totally driverless automobiles, and even ones with autonomous options (emergency braking, lane departure avoidance, and so forth.), are inclined to hackers.
“There are various methods for the driverless car story to unfold over the following a number of years. It’s vital for insurers to fastidiously watch the development to assist put together purchasers–each customers and companies,” stated Gaurav D. Garg, CEO private insurance coverage, AIG.
The human ingredient in self-driving automobiles doesn’t simply finish with whether or not or not folks will purchase them. Some auto producers additionally fear about how people will deal with driverless automobiles. Dietmar Exler, chief govt of Mercedes-Benz USA, is anxious that people will “bully” driverless automobiles. When requested what’s taking so lengthy to develop self-driving automobiles, he stated, “It’s not expertise, that’s advancing quick. It’s not insurance coverage and legal responsibility points. I do imagine in attorneys. I’m a lawyer myself. We’ll clear up these points out. The true difficulty is people.”
Volvo shares the identical concern about bullying and determined to maintain its early fleet of check automobiles in London unmarked in order that they don’t look any completely different from a traditional Volvo automobile.
And final however not the least, there are issues concerning the ethics and morality of clever machines. The Massachusetts Institute of Expertise (MIT) is gathering a human perspective on ethical choices made by machine intelligence, comparable to self-driving automobiles, with a venture titled “The Ethical Machine.” The net survey generates ethical dilemmas, the place a driverless automobile should select the lesser of two evils, comparable to killing two passengers or 5 pedestrians. As an out of doors observer, folks choose which consequence they suppose is extra acceptable. “Assist us learn to make machines ethical,” the introductory video asks.
The takeaway for insurers
There’s a lot happening within the race for self-driving automobiles. The ecosystem round it’s huge and complicated. Whereas it might not imply that auto insurance coverage might be out of date anytime quickly, carriers can be smart to start out interested by the shift in tradition it can require and put together themselves for the incoming disruptors. Whether or not totally automated driverless automobiles launch as early as 2019 or take till 2035, the carriers making the primary strikes to harness large information and type the essential partnerships would be the ones taking the lead in autonomous automobiles.
Additional studying on self-driving automobiles:
Insuring Autonomous Automobiles
How Will Driverless Automobiles Change the Auto Insurance coverage Business